Advantages and Disadvantages of the Keto Diet—a Comprehensive Guide
The ketogenic diet, in short, keto, is one of the most popular diets at the moment. It has been around for about 100 years. Initially, it was the go-to diet for people with epilepsy, but it has since become a real dieting trend. So what are the advantages and disadvantages of the keto diet, and what makes it so popular? Is it really a diet that everyone can use, or should we exercise more caution? We’ll cover all this and more.

What is the keto diet?
The ketogenic diet, also known as keto, is a diet that eliminates almost all carbs and replaces them with fat. As a result of such a low-carb, high-fat diet, the body goes into a state called ketosis.
When you’re in ketosis, the body produces ketones, which it uses as an energy source. In other words, your body is no longer using carbs, or glucose, as energy, but fat.
All this is not new. Its history began in 1921 when endocrinologist Rollin Woodyatt discovered that the human body produces ketones when it gets very few carbs.
In the same year, Russel Wilder of the Mayo Clinic used this discovery to create the ketogenic diet and try it as a treatment for epilepsy.
More research followed in the 1960s and 1970s. All studies showed the keto diet had positive effects on children with epilepsy.
In the 1970s, studies focused on increasing the number of carbs without stopping ketosis to give children and their parents more freedom and variety in their diets.
At the moment, we know that a keto diet can also reduce blood sugar levels and positively affect those struggling with insulin resistance.

Types of Keto Diets
Keto comes in various shapes and forms.
- The standard ketogenic diet (SKD) involves getting about 70% of your calories from fat, 20% from protein, and only 10% from carbs. It is the most common and typically used in conditions like epilepsy, though modern diet culture has also seen it extend to the general population.
- The high-protein keto diet is similar to SKD but requires getting only about 60% of your calories from fat, with 35% coming from protein and the remaining 5% from carbs.
- The cyclical ketogenic diet allows periods with higher carbs. For instance, you may choose to follow a standard keto diet 5 days a week and eat more carbs during the other 2.
- The targeted keto diet allows you to add carbs when you work out.
Only the first two types have been studied for their health benefits. The last two are more common among athletes and bodybuilders. The high-carb periods may also prevent you from going into ketosis or, at the very least, briefly take you out of it.
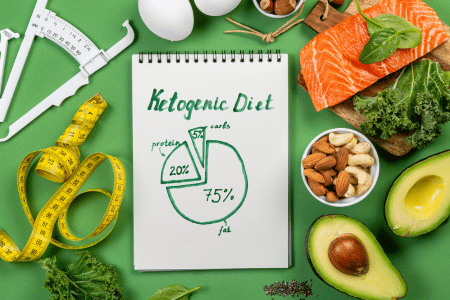
Keto diet advantages and disadvantages
Keto diets help your body go into ketosis and burn fat. Studies have proven they’re a real asset for people with epilepsy. They’re not a one-size-fits-all and are not sustainable for everyone. Here are the main pros and cons of keto diets.
Pros
1. They help people with epilepsy
The number one benefit and the reason ketogenic diets exist is to help people with epilepsy. The disease, which causes seizures and can significantly alter the quality of one’s life, affects about 50 million people worldwide.
While most of those people can use medication to reduce seizures, these meds are ineffective for about 30% of them.
Starting in 1921, many studies have shown ketogenic diets can drastically reduce the number of seizures, especially in children.
2. Improved blood sugar and insulin management
Eating fewer carbohydrates but more fat and protein can help you manage blood sugar levels. Studies even show that keto is a good diet for people with diabetes.
Some say it could help those with type 1 diabetes as well, though the studies are not as conclusive.
3. Quick weight loss
Weight loss is the number 1 reason people consider going on a diet, and keto certainly delivers good results.
Studies show this result is because of various factors, such as reduced appetite and increased fat-burning.
One thing worth noting is that you need to stick to keto long-term if you want lasting results. When you switch to keto, especially if you eat a high-carb diet, you will see results quickly.
But for those results to last, you’ll need to stick to keto, which many could find difficult.

4. May boost athletic performance
Some forms of keto can help athletic performance. Athletes who follow a diet that allows them to go into ketosis burn more fat and may even build muscle quicker.
Some may find the lack of carbs difficult, especially when doing strenuous exercises, so tread carefully.
5. It may help with other health conditions
Epilepsy and diabetes aren’t the only health conditions that could benefit from keto. Some of these include:
- Alzheimer’s disease
- Parkinson’s disease
- Certain forms of cancer
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
- Brain trauma
- Migraines
Studies in these areas are still ongoing, so be sure to talk to your doctor before trying keto for one of these conditions.

Cons
Despite the seemingly long list of benefits, a keto diet is not for everyone. It is challenging to keep up with, can be very expensive, and can have serious side effects.
When you start keto, while your body goes into ketosis, you’ll most likely experience the “keto flu,” which comes with symptoms such as:
- Fatigue
- Weakness
- Irritability
- Insomnia
- Gastrointestinal issues
- Intolerance to effort
- Headaches
These symptoms should subside within a few weeks, but if they don’t, you’ll probably need to stop doing keto.
This type of diet is also not the best if you:
- Have a history of eating disorders
- Have liver or thyroid issues
- Have pancreatic or gallbladder diseases or if you had your gallbladder removed
Those who have kidney issues should also tread carefully; as kidney stones are a known risk of long-term keto.
On top of that, there are a few more complications that could arise, even if you’re perfectly healthy.

1. Nutritional deficiencies
Keto excludes entire food groups. With only 10% of your calories from carbs, you won’t eat many fruits, starches, legumes, or vegetables.
That’s why vitamin C, magnesium, zinc, and more deficiencies are common for those on keto. Supplementing may help, though, in time, it might all become difficult to sustain.
2. High cholesterol
Keto is almost always high in animal fat. While some fat in your diet is healthy and necessary, too much of anything can harm you.
One solution could be keeping saturated fats low and replacing them with monounsaturated ones. Unfortunately, there isn’t enough research to support this idea.
3. Heart disease
High cholesterol can lead to heart disease. It is a downward spiral you don’t want to get caught on. So if you’re trying keto, regardless of the reason, stay in contact with your doctor, and make sure your diet isn’t causing more harm than good.
Leaning more towards plant-based fat and “vegan keto” could be a solution. But as we’ll see in a moment, that also comes with certain challenges.
4. It may disrupt your hormones
Some hormonal conditions, like polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), may benefit from keto. That’s true, especially when the main cause behind the syndrome is insulin resistance, as ketosis can help balance blood sugar levels.
However, the diet is highly restrictive and may disrupt hormones, leading to irregular cycles and even amenorrhea. It’s the reason some doctors don’t recommend it to those trying to get pregnant, for instance.

Can you do keto if you’re vegan?
Yes, vegan keto is possible, but it is not an easy diet. Plant-based foods are naturally higher in carbs, so you must be careful when creating your meal plan. Foods like avocados, nuts, nut butter, and coconut oil will need to be your staples at all times.
The list of permitted foods is much smaller for vegan keto than for the traditional one, but it is still possible to go into ketosis. Just make sure you’re eating enough and watch for symptoms that could signal a nutritional deficiency.
Vegetarian keto, which allows you to eat eggs and grass-fed butter on top of the vegan fats, is more manageable and offers more variety.

Key takeaways
Keto is a high-fat, low-carb diet that allows your body to go into ketosis and burn fat instead of glucose for energy. It was initially a diet created for those with epilepsy, and to this day, it is used to help those who don’t respond well to anti-seizure medication and children with the condition.
Since 1921, many people have looked into the keto diet's advantages and disadvantages, turning it into the popular diet it is today.
Keto helps with weight loss and blood sugar management, may boost athletic performance, and help with certain conditions such as Alzheimer’s.
Despite all this, it is not a one-size-fits-all diet and, in the long term, can cause more harm than good. Some of its side effects include nutritional deficiencies, kidney stones, heart disease, and hormonal imbalances.
If you decide to try keto and want to supplement to prevent nutritional deficiencies, check out some of our daily multivitamins that are perfect for those times when your diet is not the most balanced and you need an extra boost.

Health/Medical Disclaimer
This blog post does not provide health or medical advice. This blog post is for informational and educational purposes only and is not a substitute for professional health or medical advice. Before taking any actions based upon such information, we encourage you to consult with the appropriate medical and healthcare professionals. We do not provide any kind of health or medical advice. The use or reliance of any information contained on this blog is solely at your own risk.
Sources
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19049574/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6251269/
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/epilepsy
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26355236/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32173786/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27623967/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7705738/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29737587/
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1186/1550-2783-9-34
https://www.nature.com/articles/ejcn2013116
Recent Posts
-
Are sunscreen ingredients harmful?
Sunny days can bring a lot of fun. Going out for a swim, spending time in nature, or relaxing on the …18th Mar 2024 -
The Veggie Debate: Does Cooking Vegetables Destroy Nutrients and the Best Ways to Cook Them
Vegetables are one of the healthiest foods you can choose. Some people downright hate them, while so …4th Mar 2024 -
Best Foods for COVID Recovery and Prevention
A few years ago, a new virus took the world by surprise. COVID-19 may look like the flu on the surfa …19th Feb 2024




